APPLICATION OF PRIM' s AND KRUSKAL' s ALGORITHM IN REAL-LIFE SCENARIOUS
Welcome! Let’s start with some informal context. Let me ask you something:
Have you ever used Google Maps for directions?
Have you ever used Social Media apps like Facebook or Instagram?
Well, guess what, you have been using graphs all along. Let’s see what these
algorithms actually are and how they work!
If “Yes” to any of these
questions, then you’ve definitely used graphs and you didn’t even know it! Surprised?
I was, too!
Through this blog, we will go through two essential, yet fun
algorithms and compare them in real-world scenarios.
Let’s say our task is to find minimum path from current location to destination in such a way that we need to find out all the paths and from this we need to find minimum path and the minimum cost of path. Now how do we find that out? We can use Prim’s Algorithm or Kruskal’s Algorithm.
v Both Prims and Kruskal Algorithms are used to find the minimum spanning trees. So now, what is Minimum Spanning Tree?
MST is used to decide path which gives minimum cost to apply daily life concepts like travelling, salesman's problems, electrical wiring, etc. So here we show how minimum cost is calculated in minimum spanning tree using different algorithms like prim's and kruskal's algorithm.
v Now the applications of the Kruskal and Prims Algorithm are basically the applications of minimum spanning tree. Both approaches are known as ‘greedy’ algorithms. So now What is a ‘greedy’ algorithm?
It is called greedy because it chooses the optimal solution present at the moment and not the optimal solution as a whole. In greedy algorithms, at every step, there is a choice that is optimal for the problem up to that step, and after the last step, the algorithm produces the optimal solution of the complete problem.
In Prim’s algorithm, you always
keep a connected component, starting with a single vertex. Prims algorithm
finds minimum cost spanning tree by selecting edges from graph one by one. It
starts with tree T consisting of vertex x. Then it adds shortest edges edge
emanating from x that connects to T to rest of graph. It then moves further and
repeat process.
In Kruskal’s algorithm, it finds the minimum cost spanning tree of graph by adding edges one by one. However, Kruskal's algorithm form a forest of trees which are joined together incrementally to form minimum cot spanning tree.
Now I recommend you all to go in the technical of both the algorithms through other blogs and learn the difference in the implementations of both.
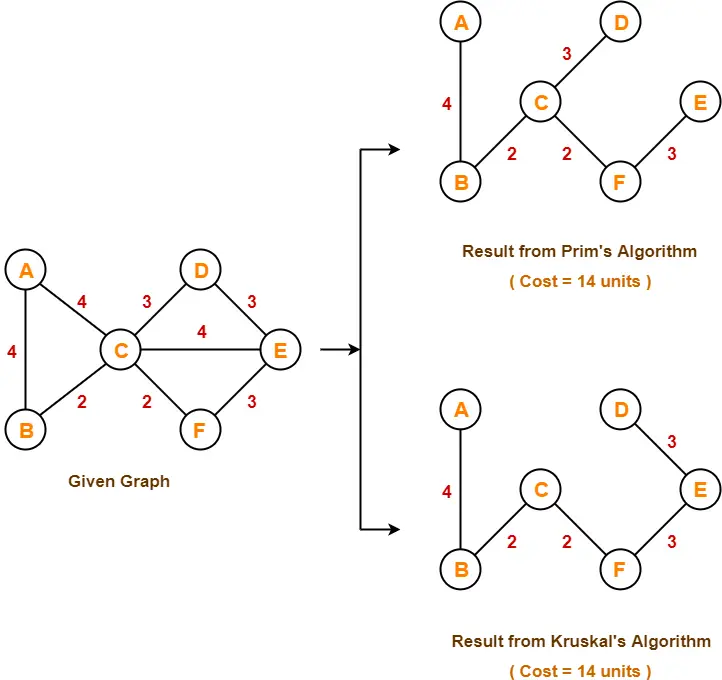
Comparison of
the two algorithms
Minimum spanning tree application in the currency
market :
1. Currency Market
v
Recently,
a lot of authors have focused on graph-theoretical representation and analysis
of the financial market.
v
Best
approach: - Scientist had chosen minimum spanning tree research in currency
market. Because it is best data type suitable for currency market.
2. Social
Media
v
Everyone has used social media sites. In social media we have
our network i.e we connect with our friends.
v
Many a times social sites suggests us to send a connection
request to a person we might know but haven’t sent the request and it also show
how many mutual friends are there between you and the person you are sending
the connection request.
So have you ever wondered how this works internally.
Basically it uses the graph data structure
- Applications where Kruskal’s algorithm is
generally used:
1. Landing cables
2. TV Network
3. Tour Operations
4. LAN Networks
5. A network of pipes for
drinking water or natural gas.
6. An electric grid
7. Single-link Cluster
- Applications where Prim’s algorithm is
generally used:
1. All the applications stated
in the Kruskal’s algorithm’s applications can be resolved using Prim’s
algorithm (use in case of a dense graph).
2. Network for roads and Rail
tracks connecting all the cities.
3. Irrigation channels and
placing microwave towers
4. Designing a fiber-optic grid
or ICs.
5. Travelling Salesman Problem.
6. Cluster analysis.
7. Pathfinding algorithms used
in AI(Artificial Intelligence).
8. Game Development
9. Cognitive Science
Thank You !
Authors
Vishwakarma Institute Of Technology, Pune.
Second-Year Students, Computer Department
Achwale Prajwal Namdevrao
Devshatwar Shruti Rangnath
Jotrao Rutuja Sanjay
Motbhare Subodh Uddhav
Shaha Shraddha Shrenikkumar


Comments
Post a Comment